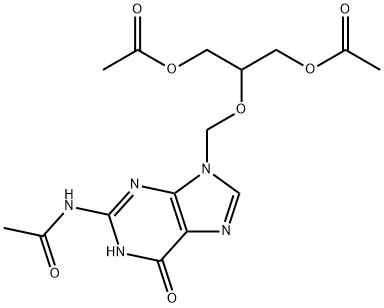
Understanding Triacetyl-ganciclovir: A Key Compound in Antiviral Therapy
2024-08-07
In the realm of antiviral research and treatment, compounds are constantly being developed and refined to combat various viral infections. One such compound is triacetyl-ganciclovir, a derivative of ganciclovir with specific applications and properties that make it a notable subject of study. In this blog, we will delve into what triacetyl-ganciclovir is, its significance in antiviral therapy, and its potential applications.
1. What is Triacetyl-ganciclovir?
Triacetyl-ganciclovir (TACV) is a chemical derivative of ganciclovir, an antiviral medication used primarily to treat infections caused by cytomegalovirus (CMV) and other herpesviruses. The modification of ganciclovir to create triacetyl-ganciclovir involves adding three acetyl groups to the ganciclovir molecule.
2. Why Triacetyl-ganciclovir?
Triacetyl-ganciclovir was developed to improve upon the properties of ganciclovir. The acetylation process enhances certain aspects of the compound, making it a useful tool in various contexts:
- Enhanced Bioavailability: Triacetyl-ganciclovir often exhibits improved absorption and bioavailability compared to ganciclovir. The acetyl groups can make the compound more lipid-soluble, facilitating its passage through cellular membranes and potentially increasing its effectiveness.
- Reduced Toxicity: The acetylation of ganciclovir can modify its pharmacokinetic profile, which might help reduce toxicity and side effects associated with ganciclovir treatment. This could lead to a more favorable safety profile for patients.
- Prodrug Characteristics: Triacetyl-ganciclovir acts as a prodrug, which means it is converted into the active form (ganciclovir) within the body. This conversion can help in optimizing the delivery and release of the active drug in targeted tissues.
3. Applications and Potential Benefits
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infections: Triacetyl-ganciclovir can be used in the treatment of CMV infections, particularly in immunocompromised patients such as those with HIV/AIDS or organ transplant recipients. Its enhanced properties could offer better control of these challenging infections.
- Research and Development: The compound is of interest in antiviral research due to its modified properties compared to ganciclovir. Researchers investigate TACV to understand its efficacy, safety, and potential benefits over existing antiviral drugs.
- Pharmaceutical Development: TACV’s improved bioavailability and reduced toxicity make it a candidate for further pharmaceutical development. It may be considered for new formulations or treatment regimens that leverage its advantageous properties.
4. Current Research and Findings
Ongoing research is focused on evaluating the full range of benefits and limitations of triacetyl-ganciclovir. Studies aim to determine its effectiveness in treating viral infections, its safety profile, and any potential advantages over ganciclovir and other antiviral agents. This research is crucial in advancing antiviral therapy and ensuring that new treatments offer tangible benefits to patients.
5. Conclusion
Triacetyl-ganciclovir represents an important step in the evolution of antiviral medications. By modifying the ganciclovir molecule, researchers have developed a compound with potentially enhanced bioavailability and reduced toxicity, offering new possibilities in the treatment of viral infections, particularly those caused by CMV. As research continues, triacetyl-ganciclovir may play a significant role in advancing antiviral therapy and improving patient outcomes.
Stay tuned for more updates and discoveries in the field of antiviral research, and keep an eye on how compounds like triacetyl-ganciclovir could shape the future of treatment for viral diseases.